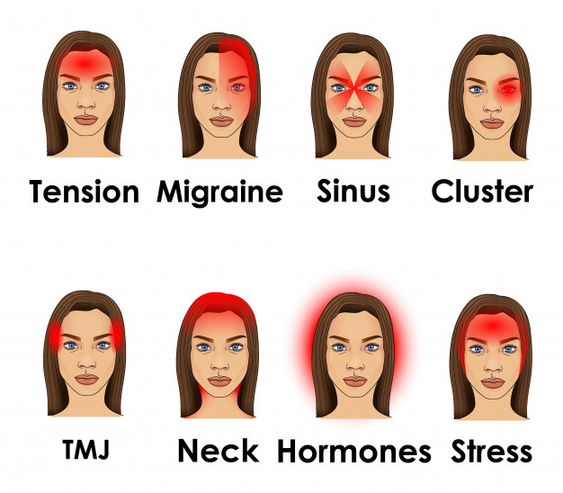
We all have different kinds of headaches, but we are never able to differentiate. There are several types of headaches with different underlying causes related to them. Headaches are broadly categorized into two categories:
- Primary Headache
- Secondary Headache
Migraine headaches
Migraine is manifested as a throbbing type of headache, usually on one side of the head. Each episode may last from 4 hours to 3 days. The frequency of the episodes may vary from several times a week to once a year. In addition to the headache, the following symptoms may also be associated:
- Increased sensitivity to light, sound, and smell
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal discomfort
- DizzinessBlurry vision
- Numbness
A migraine attack can be triggered by the following conditions:
- Stress and anxiety
- Sleep disruption
- Bright light
- Loud noise
- Dehydration
- Skipping meals
- Hormonal changes
- Over-The-Counter medications like ibuprofen or aspirin
Following medications are usually prescribed to prevent migraine attacks.
- Anti-seizure medications such as topiramate and valproic acid are advised to help to calm down the nerve cells in the brain.
- Beta-blockers — These are usually prescribed in cases of hypertension and heart-related disorders. It may also be prescribed in cases of migraine to improve the blood flow. Some examples of beta-blocker drugs are metoprolol, propranolol, and timolol.
- Antidepressants — These drugs have an influence on the serotonin levels secreted in the brain. Some of them include amitriptyline and venlafaxine.
- CGRP Inhibitors — CGRP that is calcitonin gene-related peptide is a chemical substance responsible for migraine pain. CGRP inhibitors such as erenumab, aimovig and fremanezumab have been approved to prevent the migraine attack.
- Triptans — These drugs are mostly used to treat migraine headaches. Frovatriptan helps in the prevention of migraine that occurs due to the menstrual cycle by affecting the serotonin levels.
Tension headache
These are the most common type of headache experienced by people. This is manifested as a constant dull pain on both sides of the head. The headache may also be associated with:
- Pressure behind the eyes
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Radiating pain to the face, head, neck, and shoulders.
The causes may include stress, anxiety or depression and the triggers usually involve:
- Lack of sleep
- Lack of physical activity
- Loud noise
- Dehydration
- Skipped meals
- Reduced eyesight
Tension headache is broadly classified into two types:
Episodic — The headache occurs in less than 15 days per month.
Chronic — The headache occurs after more than 15 days per month.
These can be prevented by :
- Regular physical activity
- Proper sleep
- Adapting to right body postures
- Regular eye checkup
- Treating stress, anxiety or depression, if these are present
- Meditation
Other than the above measures, over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen and aspirin.
Cluster headache
These are severe piercing and burning types of headache, surrounding one eye or on one half of the face. This may also be associated with nasal congestion, eye tearing, swelling, redness, perspiration on the affected side. Other than this, there may be restlessness and increased sensitivity to light and noise. Each episode can last for 15 minutes to 4 hours a day. A person may experience a series of 1–4 episodes in a day. Cluster headache is more common in men than in women. It is also more common in smokers that non-smokers. It is more likely to occur in spring and fall.
Some unique features of cluster headache:
- Cluster headache worsens within a short span of 5 to 10 minutes with high intensity.
- The pain occurs always on one side and remains on the same side during the period when a person experiences the headache every day.
- The pain can also be pulsating sometimes.
- Each episode usually lasts for 30 to 90 minutes and the frequency of the episodes may differ from once every other day to 8 times a day.
- The headache generally occurs on a regular basis at the same time of the day, which is why it is also known as “alarm clock headache”.
- There is a period of remission after the headache occurs regularly for about 2 weeks to 3 months.
For the treatment, the doctor usually advises oxygen therapy, sumatriptan or any local anesthetic to relieve the pain. It is only after the final diagnosis is done, the preventive plan is made. Some of the Best Neurologists in India with the help of Medserg believe that corticosteroids, melatonin, topiramate, and some calcium channel blockers help in putting the cluster headache into remission or symptom-free period.
Following medications are prescribed by neurologists to provide relief:
- Verapamil
- Opiramate
- Steroids
- Melatonin
- Lithium
Sinus headache
Sinus headaches are usually a result of an allergic reaction. There is a dull, throbbing, constant pain revolving around the sinus area and on the front side of the head. Other associated symptoms are:
- Blockage of nose
- Thick green or yellow nasal discharge
- Fever
- Nausea
- Increased sensitivity to light and sensitivity
It is often confused with a migraine headache. A person having chronic seasonal allergies, sinus infection or sinusitis is prone to sinus headache.
It is treated by clearing the mucus that has been built up leading the sinus pressure. Most commonly used medications are nasal steroid sprays, over-the-counter decongestants like phenylephrine, and antihistamines like cetirizine. In rare cases, sinus surgery may also be needed to remove the polyps or open up the swollen sinuses.
Hormone-related headache
This most commonly occurs in women due to hormonal changes especially during menstruation, while taking birth-control pills or during pregnancy. The headache that is especially associated with menstruation is known as menstrual migraine. Pain relievers such as naproxen or frovatriptan can be used to manage the pain. Other than this, relaxation methods like yoga, acupuncture or meditation may also be used.
Hypertension-related headache
This is caused by raised blood pressure and indicates an emergency situation. This is experienced only when the blood pressure levels are alarmingly high. It usually occurs on both sides and gets worse while doing any physical activity. This can also be associated with changes in vision, numbness or tingling, breathlessness, nosebleeds, and chest pain. Immediate medical attention is needed in such cases. The objective of the treatment is to lower down the levels of blood pressure.
Rebound headache
The rebound headache occurs due to high dosage of medication. This is a dull, constant type of headache which may be slightly more intense than the tension headache. People who excessively use pain killers are more prone to rebound headaches. For example, over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, naproxen, etc being used for more than 15 days in a month. The only advised treatment is to reduce or taper down the number of painkillers taken. The pain may get worse at first and gets controlled later.
Head injury-related headache
This type of headache occurs after a person suffers from a head injury. The symptoms are similar to migraine or tension-like headache and last up to 6 to 12 months.
Medications prescribed are triptans, sumatriptan, beta-blockers, and amitriptyline are most commonly used to control the pain.
Exertional headache
Intense physical activity is the main cause of exertional headache. These physical activities include weight lifting, running, and sexual intercourse, which act as triggering factors. It is said that these activities increase the blood blow to the head leading to a throbbing type of headache.
An exertion headache usually lasts for a few minutes to several hours. Pain relievers such as aspirin and ibuprofen can relieve the symptoms.
Caffeine-related headache
Excessive consumption of caffeine, about more than 200 mg per day can lead to headaches. The headache takes place nearly 24 hours after abruptly stopping the coffee consumption. It is associated with tiredness, difficulty in consumption, poor mood, nausea, and irritability.