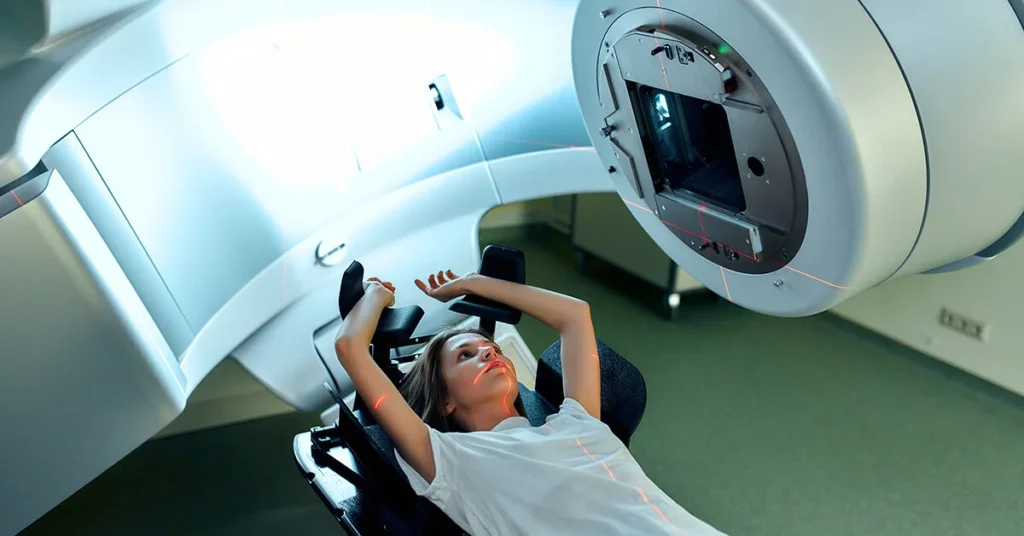
If you are diagnosed with brain tumor and your oncologist recommends ‘stereotactic radiosurgery’ (SRS), most likely this may set your heart racing. The very mention of ‘stereotactic radiosurgery’ conjures up images of you being surrounded by a team of doctors using specialized complex instruments to operate upon you. You imagine that such a complex surgery will involve an inordinate amount of time. You may also believe that you will be in the hospital for a long time.
The reason you are being recommended to undergo an SRS is either because your tumor is difficult to reach or it is close to the vital organs. Also, it could be that your tumor(s) has/have moved within the body. So, except for the use of sophisticated equipment, the other things about stereotactic surgery are not what your imagination tells you. Firstly, SRS is not an invasive surgery. It does not involve any incision/cut to the brain, unlike conventional surgery. SRS is the use of specialized, highly-focused radiation at high doses to specifically treat brain tumors and functional abnormalities in the brain. Sometimes, SRS is used to treat tumors in the lungs, spine, neck, liver, and other parts of the body too. In this case, it is called Stereotactic Body Therapy.
The SRS technique uses advanced imaging technologies along with sophisticated computer guidance to deliver a highly targeted and intense dose of radiation. Also, the treatment is not as time-consuming as it may lead one to believe. It takes anywhere from an hour to four hours and is an outpatient procedure. Compared to traditional radiation therapy, it sometimes takes only one or fewer treatments of SRS. SRS is increasingly being recommended to patients having up to three brain tumors that are less than three cm in diameter. SRS does not remove the tumor, but it damages the DNA of tumor cells. Resultantly, these cells lose their ability to reproduce. From the commencement of the treatment, benign tumors usually shrink between 1.5 years to two years. Metastatic and malignant tumors may shrink faster in a couple of months. As per clinical studies, the side effects of this procedure are fewer than conventional surgery. Not just to treat tumors, SRS can be administered to kill any remaining tumor cells that the surgeon may have missed during the surgery.
Who can opt for Stereotactic Radiosurgery?
Stereotactic Radiosurgery is recommended for patients;
- Whose tumors are not surgically accessible or are at a substantially advanced stage.
- Who are too old to undergo conventional surgery.
- Who cannot tolerate anesthesia?
Advantages of Stereotactic Radiosurgery
- Patients with brain tumors are known to have less cognitive deterioration after treatment.
- As there is no physical incision, the risk of complication is also reduced.
- It treats multiple tumors simultaneously.
- An SRS treatment does not require prior hospitalization as is done in conventional surgery.
- Preserves healthy tissues, as the therapy is guided to targeted areas with extreme precision.
- Hospitalization is short and in rare cases will need an overnight stay.
- Recovery from a stereotactic radiosurgery procedure is faster.
What Other Conditions Does SRS Treat?
Other than treating brain tumors and any residual tumor cells post-surgery, SRS is administered to treat the following conditions:
- Arteriovenous Malformations
- Cancers in the eye
- Epilepsy
- Neurological Problems
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Pituitary Tumours
Impact of Stereotactic Radiosurgery on Brain Tumor Treatment
As is known, an SRS is a highly specialized treatment for brain tumors. Its effectiveness lies in the precise targeting of the tumors and inflicting little to no damage to the adjacent tissues. SRS is recommended for patients with up to three brain metastases. SRS treatment aims to eliminate tumors or stabilize and shrink them so that they are ineffective after treatment. As it is a treatment that can be completed in one day, it also does not interfere as much with the delivery of chemotherapy.
A distinct impact of SRS on brain tumor treatment is that it causes less cognitive deterioration in patients. This was the finding of an 11-year-old study. It was undertaken on a group of 111 patients assigned SRS only and 102 patients who were assigned SRS followed by Whole Brain Radiation Therapy (WBRT). There was less cognitive deterioration at three months in patients treated with SRS alone. The Quality of Life was also higher in this group at three months. The functional independence at three months was not significant between the two groups.
Brain Tumour Treatment in India
Brain tumor treatment in India is offered at reputed hospitals in the major cities. India’s location as a prominent South Asian country and its developed healthcare facilities and world-renowned medical professionals makes it a chosen destination for medical treatment
Radiosurgery treatment in India is also among the best in the world. The latest in stereotactic radiosurgery is Proton Beam Therapy (PBT), which is at present only offered by a popular hospital chain in the country. As one of the most affordable places for stereotactic radiosurgery treatment in the world, increasingly more and more foreign patients are flying to India. The treatments here are offered at 1/6th of what it costs in other countries. Some of the treatments and their associated indicative costs are as follows:
- CyberKnife Radiosurgery: $6800-$8000
- Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: $5800-$6500
- Linear Accelerator: $6500-$8000